Plot Hull Plot for Factor Analysis
plot.Hull.RdThis function creates a Hull plot to visualize the relationship between the Comparative Fit Index (CFI) and the degrees of freedom (df) for a range of models with different numbers of factors. The Hull plot helps in assessing model fit and identifying optimal models.
# S3 method for class 'Hull'
plot(x, ...)Arguments
Value
None. This function is used for side effects (plotting).
See also
Examples
library(EFAfactors)
set.seed(123)
##Take the data.bfi dataset as an example.
data(data.bfi)
response <- as.matrix(data.bfi[, 1:25]) ## loading data
response <- na.omit(response) ## Remove samples with NA/missing values
## Transform the scores of reverse-scored items to normal scoring
response[, c(1, 9, 10, 11, 12, 22, 25)] <- 6 - response[, c(1, 9, 10, 11, 12, 22, 25)] + 1
# \donttest{
Hull.obj <- CD(response)
#>
CD is simulating data: nfact= 1/10
CD is simulating data: nfact= 2/10
CD is simulating data: nfact= 3/10
CD is simulating data: nfact= 4/10
CD is simulating data: nfact= 5/10
CD is simulating data: nfact= 6/10
CD is simulating data: nfact= 7/10
CD is simulating data: nfact= 8/10
#> The number of factors suggested by CD is 7 .
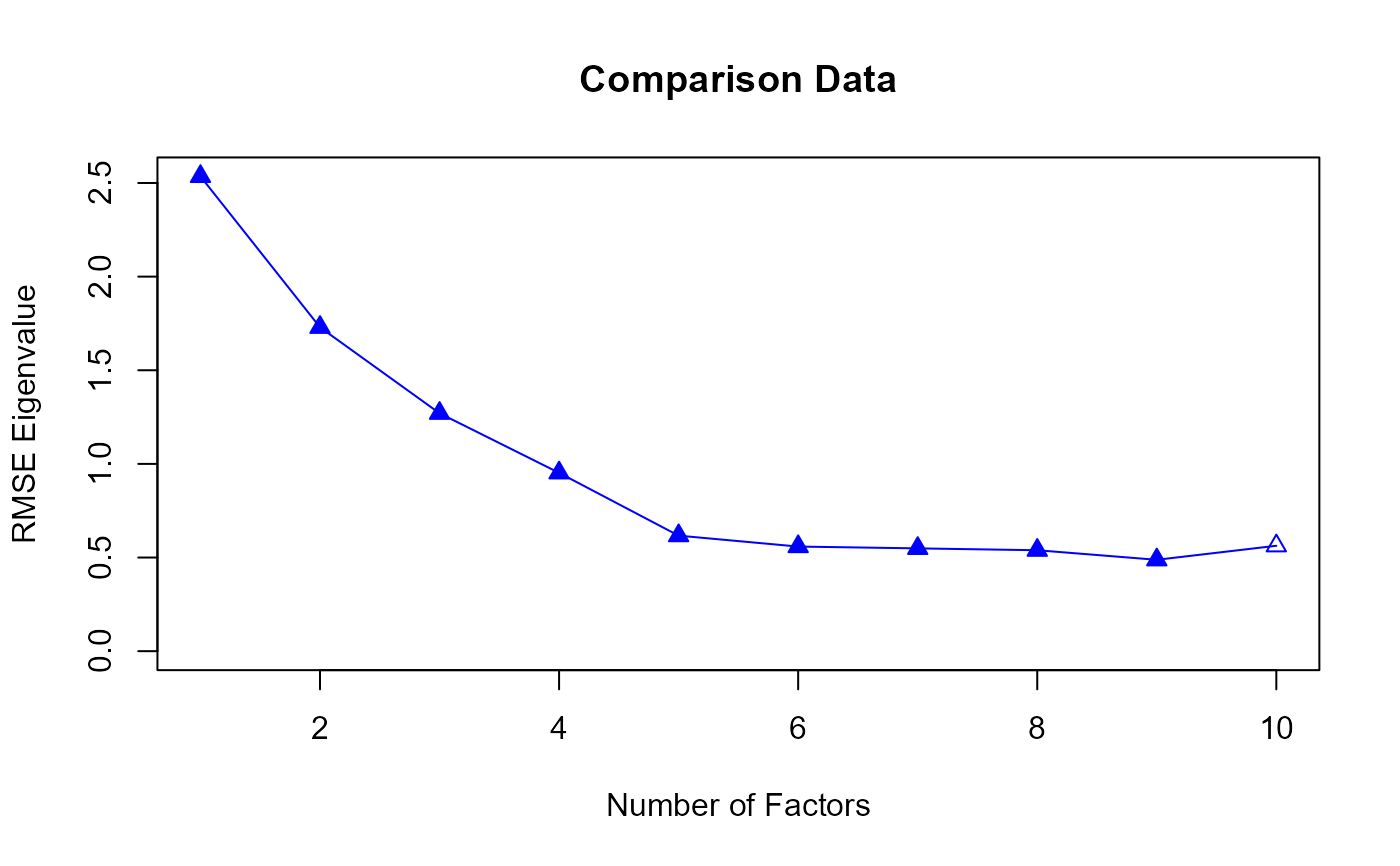 ## Hull plot
plot(Hull.obj)
# }
## Hull plot
plot(Hull.obj)
# }